Furloughed workers and what that means for unemployment
This article focuses on the fact that ‘unemployment rate rose to 7.3 percent’ in America due to the ‘furloughed federal workers being counted as unemployed.’ The government shutdown led to workers out of a job.
The shutdown was temporary yet the furloughed workers had been counted in the latest unemployment report, leading to the increased percentage of unemployed. Unemployment is defined as: ‘People of working age who are without work, available to work, and actively seeking employment” The unemployment rate is the number of people who are unemployed expressed as a percentage of the total labor force. Conversely there are two criteria to be counted in the percentage of unemployed, these are: (i) people must have no job (ii) they must be actively seeking employment. Those who do not have jobs and are not actively searching are considered to be out of the labor force.
Considering the nature of the government shutdown, the federal workers should not have been counted towards the unemployment rate. This is because the shutdown led to a temporary leave, suggesting that the federal workers were not actively searching for a new job. This is where hidden unemployment comes in. Hidden unemployment consists of several different groups of people. The group of unemployed individuals that are not counted in the unemployment figures compiled and released by the government. This group exists because the official unemployment figures only include people that are unemployed, but actively seeking a new employment opportunity.
It has been said that ‘Employers added an average of 202,000 jobs from August through October’ this suggests that there are enough jobs available in the economy, but the workforce is either unable or willing to take the jobs which are available to them. It is known as equilibrium unemployment or natural unemployment. It is when the labor market is equilibrium without demand deficient or real wage unemployment, yet people are still unemployed. There is equilibrium because the number of job vacancies in the economy is the same as the number of people looking for work.
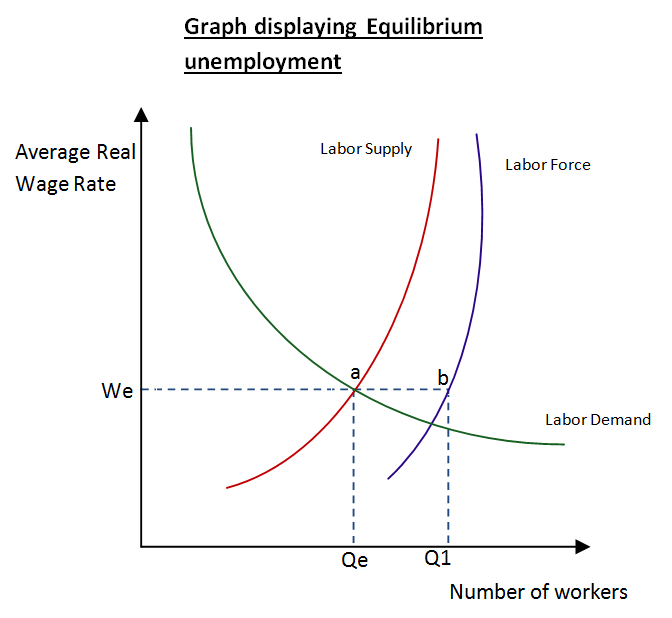
The diagram above displays a measure of the total Labor force (LF). It shows that the Labor force is greater the Labor supply (ASL) due to the labor supply comprising of people able and willing to work. The ASL shows the number of people willing and able to work at the given wage rate (We). However at the given wage rate there will be more workers looking for a job than those actually working. Point Qe shows the number of workers that are willing to take a job at the wage rate. Q1 is the labor force available. Thus unemployment of a–b exists in the market.
The graph shows that the unemployed in the market, a-b, are not willing to or able to take the jobs that are available. The article states ‘the percentage of Americans working or looking for work fell to a fresh 35-year low’ suggesting that at the current wage rate there is less incentive for people to go out and acquire jobs rather than living off unemployment benefits. This can be seen because as the wage rate increases the gap between the ASL and LF greatly reduces. Another possibility is the workers do not have the required education to apply to the jobs which are available to them. Or the jobs which are available lack proper awareness.
There are solutions for the government to use in order to reduce the unemployment rate. If the people have little incentive to find a job if the unemployment benefits available to them in their country are generous, a classical economic approach can work. Governments should lower the unemployment benefits to encourage unemployed workers to take jobs that are available. This would shift the aggregate supply of labor to the right bringing it closer to the labor force. More market based policies suggest that the government regulations reduce the flexibility of the employers. It is suggested that businesses are less willing to hire new workers due to the difficulties set by the government. Therefore deregulation of labor markets will allow businesses to hire more workers.
Interventionist policies include long term solutions involving the education system to be supported by the government allowing people to gain the proper training required for certain jobs and to be able to adapt to changing economic conditions. It is also suggested that the government should provide subsidies to business to offer training to new employees. This encourages business to hire new workers on the market such as students and young employees.
